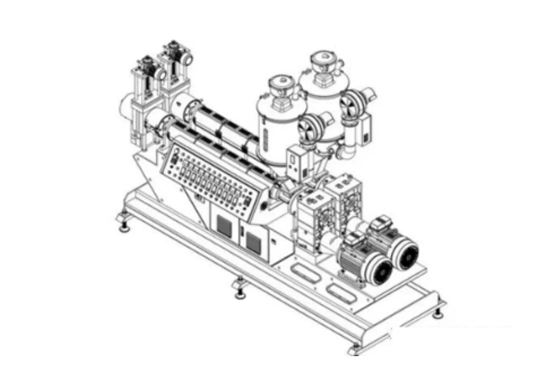
A sheet extruder machine is an indispensable machine in manufacturing, adept at crafting continuous sheets of plastic or other materials. Operating by melting raw material, it channels it through a die to shape a flat, uniform sheet. These versatile sheets find applications across diverse industries like packaging, construction, and automotive. By facilitating mass production, sheet extruders ensure efficiency and consistency, essential for meeting the demands of modern manufacturing processes. Their role underscores their significance in driving productivity and meeting the varied needs of industries worldwide.
Advantages of Sheet Extruder Machine
Dive into the world of unparalleled efficiency with Jwell's sheet extruder machine, a marvel in the realm of plastic processing. This cutting-edge machinery stands out for its remarkable precision, transforming raw materials into high-quality sheets with unmatched consistency. The Jwell Sheet Extruder, especially pc solid board extrusion line, boasts an innovative design that ensures reduced energy consumption, making it a champion of sustainability. Its user-friendly interface guarantees ease of operation, allowing for seamless production runs. Durability is another cornerstone of its design, promising long-term reliability and minimal maintenance. Whether you’re aiming for thinner films or robust sheets, the versatility of the Jwell sheet extrusion equipment meets diverse industry needs, making it an indispensable asset for businesses aiming to lead in quality and efficiency.
Functions of Sheet Extruder Machine
Jwell sheet extruder machine is a sophisticated piece of equipment designed for the plastics industry, serving a critical role in the production of plastic sheets, which are then used in a wide array of applications from packaging to automotive parts. Here’s a breakdown of its core functions:
Feeding and Melting: The first function of a sheet extruder is to accept raw plastic material, typically in the form of pellets or granules, and heat it until it melts. This process is facilitated by the extruder’s barrel and screw design, which together create the necessary heat and pressure to melt the plastic.
Mixing: Once the plastic is in its molten state, the extruder mixes it to ensure a homogeneous melt. This is crucial for the quality of the final product, as it ensures consistent color, texture, and material properties throughout the sheet.
Degassing: During the melting and mixing process, volatile compounds can be released from the plastic. A sheet extruder often includes a degassing function to remove these, preventing defects in the final product.
Extruding: The core function of the sheet extruder is to push the molten plastic through a flat die, forming a continuous sheet of plastic. The thickness of this sheet can be adjusted by changing the die gap or by altering the speed at which the plastic is extruded.
Cooling: After extrusion, the plastic sheet must be cooled and solidified. This is typically done by passing the sheet through a series of cooling rolls. These rolls not only cool the sheet but can also impart a desired texture or finish to its surface.
Polishing: Some sheet extruders include polishing rolls to enhance the surface quality of the sheet, giving it a glossy finish or a specific texture, depending on the application requirements.

 EN
EN